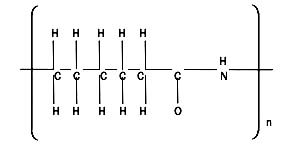
Polyamide resins are synthetic polymers containing an amide group. -CONH- , as a recurring part of the chain. This polymer was first commercially introduced by DuPont as a result of the significant research work of W. H. Carothers in the 1930s, who was conducting early extensive research efforts in polyesters and polyamides. The first important polyamide was Nylon 6/6 produced by the reaction of adipic acid (a 6-carbon dibasic acid) and hexamethylene diamine (a 6-carbon aliphatic diamine). Several structural modifications with differing temperature capabilities have become commercially available including Nylon 6/10 , Nylon 6, and Nylon 11. The latter two are so designated because of their formation from six and eleven carton amino acids. The attractive tensile strength or tenacity has, of course, led to its significant use in fiber.
Typical Applications: Gears, rollers, slides, electrical plugs and cams. High usage in fiber form.
To Place an Order or Check Status of Order, Contact...
1246 High Street, Fairport Harbor, Ohio 44077 USA

CONTACT US